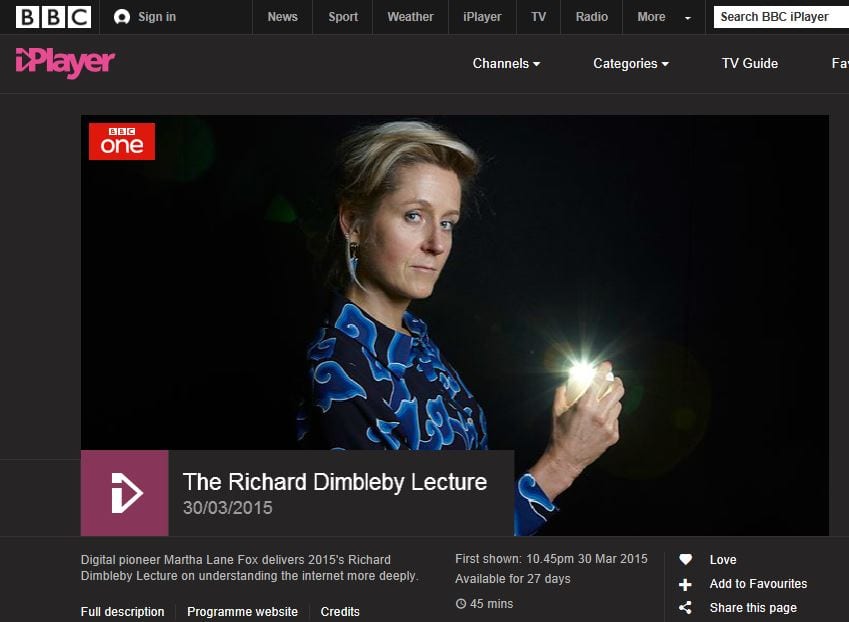
In the 2015 Dimbleby Lecture, Martha Lane Fox called for de-commercialisation of the interne (transcript) and setting up an independent body, informed by the ‘….original promises of the internet – openness, transparency, freedom and universality…’ This may be too little too late; I think the damage is already done. Amazon brings the high street to our mobile devices and we love the convenience. Twitter not only keeps us in the loop, we become the loop-makers. Whether artists, scientists or humanitists – the internet offers resources on a previously unimaginable scale. Like having a Britannica set behind every keystroke. That’s 32 volumes. RIP Britannica – 1768-2010. The day knowledge stopped for the digitally excluded.
MLF extolls the advantages of being online and says ‘Crucially, we must ensure that no one is left behind; that the 10 million adults who can’t enjoy the benefits of being online because they lack basic digital skills, no longer miss out.’ Sounds promising but… digital divides are not new. They need less talking and more genuine opportunities for challenging and bridging instead. MLF said nothing about exclusion through lack of access. Instead digital exclusion now equates to poor digital literacies iinstead.
The discourse has changed and this has been happening for some time. The focus of the Go On UK website has shifted from promoting affordable and usable technology to the quality of access without even a mention of poor broadband. The digital debate has become personal rather than political and is now about individuals. Go On replaced Race Online, also setup by MLF, with the aim of getting the nation connected for the end of 2012. At least it contained acknowledgment of digital divides. The Go On vision only addresses the lack of basic digital skills, calling this a ‘significant social issue’ – which it is – but even more crucial is the lack of internet access in the first place!
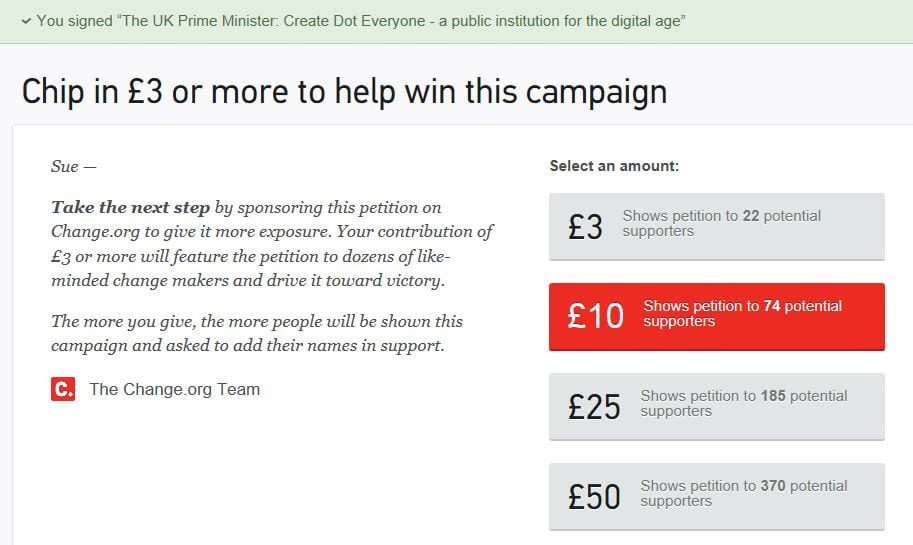
After watching and reading the lecture by MLF I signed the Dot Everyone petition calling for a public institution for the digital age. I’ll sign anything which offers opportunities to raise awareness of digital divides and exclusions. On clicking sign I was immediately asked for money in order to share my signature with others.
<#Sighs> So much for MLF’s lecture call for de-commericalisation of the internet!