The course Creativity for Learning in Higher Education #creativeHE ticks a lot of my boxes. It’s about higher education in 21st century, teaching online, creative thinking, using social media, its open, free and above all is about the digital – which at the end of the day has always been my research and passion. This blog post is my cause memory jog as much as a reflection; a questions without answers approach. Online education supports postmodern bricolage styles of learning – much of which can go unrecorded so this is an attempt to catch some of the transient experiences.
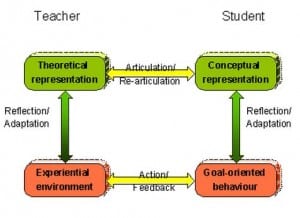
I arrived a week late! Not the best of beginnings but a well thought out course like this from Chrissi Nerantzi can take it. A good course is like a dot to dot picture. Each dot is a link. A place to go. An activity to engage with. A paper to read. In my case I haven’t yet joined them up. But I don’t have to in order to participate and learn. I’ve been selective and this is typical of the student centred approach online learning environments have to support. Capacity for multiple approaches and pathways is essential. Online design needs a holistic structure where the parts really are greater than the whole. Teaching online is about facilitation (with a capital F), about providing a mix of opportunities and supporting exploration through them. Any online teacher who tries to replicate traditional face-to-face teaching practice is likely to fail. Any online student who expects to be taught will be disappointed.
Online courses also need to understand how digital ways of working are unique to each individual taking part. Digital literacies are like fingerprints and we all have our own distinctive styles of engagement. I haven’t done as much as others but I’m not looking for accreditation which maybe supports a more fractured level of engagement. For me this is a learning experience and within the first week I have learned the following:
- I may be less creative than I think.
- Creativity is a social construct.
- Online communication is open to a variety of interpretations.
The video by Jess Haigh demonstrated the power of multimedia for online introductions. I learned so much more about Jess from seeing and hearing her than from reading text. This was a creative approach I wanted to copy. It was interesting to see the response to my comment to the group ‘Would like to post a video too but hit barriers of place, time and noise levels (excuses!)’ . It appeared to be interpreted as lack of confidence rather than lack of opportunity and demonstrated the vagaries of online communication where we see what we think rather than what is being said.
I’ve skimmed some of the reading around creativity. My first thoughts are how it sits between the subjective and objective spheres. We might produce what we consider to be creative outputs but their acceptance depends on the interpretation of others. Through the course I picked up on the #twistedpair invitation from Steve Wheeler to make unlikely pairings and relate them to teaching and learning, in my case Klimt and the Venus of Willendorf. Whether this demonstrated creativity or not can be measured by likes and tweets – but in turn these are related to access parameters and the subjectivity of others. I’ve ended the week thinking much more about creativity as a social construct and how to ‘know’ if I’m a creative person or not; I suspect I may be less creative than I think!
I have learned a lot so far and this is why I do it. Evenings, weekends, early hours of the morning. I’m a learning addict but I also want to discover how the digital can support the student learning experience. The one thing I know for sure is the process is helped where staff who teach become online students themselves first.